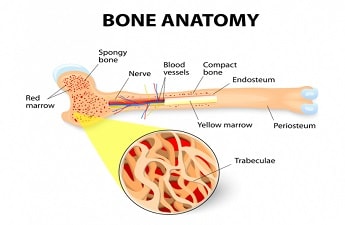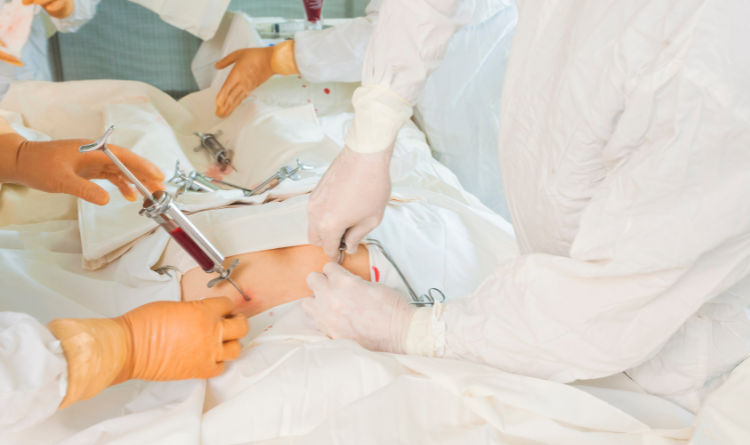
A bone marrow transplant or hematopoietic stem cell transplant is a medical procedure used to treat some cancers, immune disorders, and genetic illnesses. Red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets are all created in the bone marrow, the porous tissue found inside the bones.
Healthy stem cells are implanted into a patient's body during a bone marrow transplant to replace diseased or damaged bone marrow. The patient's own stem cells (autologous transplant) or those from a donor can both be used in the transfusion (allogeneic transplant). Preceding to control high-dose chemotherapy or radiation treatment to remove any cancerous or diseased cells, the patient's own stem cells are collected and stored in an autologous transplant. The patient's body is then given a fresh infusion of stem cells to aid in the recovery of healthy bone marrow.
Get in Touch with Medical Experts
Types of Bone Marrow Transplant
Autologous and allogeneic bone marrow transplants are the two major types –
The patient's own stem cells are obtained prior to treatment and then reinjected following high-dose chemotherapy or radiation therapy in an autologous bone marrow donation. This kind of transplant is commonly used In order to treat cancers such as lymphoma and multiple myeloma. There is no chance of rejection or graft-versus-host disease, which can happen with an allogeneic donation because the patient's own cells are used.
In an allogeneic bone marrow transplant, donated stem cells are used for treatment. These stem cells must closely seem like the tissue type of the patient to avoid immune system rejection. Family members or unconnected donors are both acceptable sources of donor stem cells. This kind of transplant is frequently used to cure genetic disorders and blood cancers like leukemia and lymphoma.
Allogeneic bone marrow transplants come in various forms, such as cord blood transplants, matched sister donor transplants, matched unrelated donor transplants, and haploidentical transplants. The choice of transplant depends on a number of factors, including the patient's age, health condition, and the availability of a suitable donor. Each type of transplant has advantages and disadvantages of its own.
Pre-Transplant Preparation for Bone Marrow Transplant
The process of getting ready for a bone marrow transplant is complicated, requiring careful planning and collaboration between the patient, their medical staff, and the donor. A few weeks or months before the transplant is due to take place, the pre-transplant preparation usually starts.
Below are the crucial actions in pre-transplant planning –
- The patient will go through a number of exams to evaluate their general health and see if they are a good prospect for the transplant.
- In order to eliminate any cancerous or diseased cells in the body, patients may endure a conditioning regimen that includes high-dose chemotherapy or radiation therapy.
- In the case of an autologous transplant, the patient's own stem cells will be taken and stored prior to the start of the conditioning program.
- If an allogeneic transplant is intended, an appropriate donor must be found and their compatibility assessed.
- Before and after the transplant, patients will be told to follow infection prevention measures, such as avoiding contact with sick people and maintaining good hygiene.
Donor Selection Process
There are usually several steps involved in the donor selection process –
-
A blood test is used to identify the patient's tissue type. Following that, prospective donors are evaluated to discover a match based on the patient's tissue type.
- The patient's medical team will search donor registries to find potential unrelated donors if a good match cannot be located among the patient's family members.
- After being identified as a prospective donor, the person is subjected to a battery of medical exams to see if they are a good candidate for donation. These examinations could involve imaging studies, physical exams, and blood tests.
- The donation procedure will begin if the potential donor is a good match and agrees to donate. Various procedures, including bone marrow extraction, peripheral blood stem cell collection, and umbilical cord blood donation, are available for the gift.
- Patients and their medical teams should make plans for the fact that the donor selection procedure may take several weeks or months to finish. A prospective donor should be completely informed about the risks and side effects of donation and receive support at every step of the way.
Stem Cell Collection
If an autologous transplant is intended, the patient's stem cells are usually taken before the conditioning regimen starts. A procedure known as apheresis is typically used to isolate the stem cells from the patient's bone marrow or peripheral blood. Blood is taken from the patient and put through a machine that separates the stem cells during apheresis. The patient's body receives the leftover blood back. After being gathered, the stem cells are frozen and kept in storage until a transplant is required.
A similar procedure known as peripheral blood stem cell collection may be used to gather stem cells from a donor if an allogeneic transplant is intended. A medication that stimulates the creation and release of stem cells into the bloodstream is injected into the donor during this procedure. Apheresis is then used to extract the stem cells from the donor's blood.
Collection Regime
A crucial step in the bone marrow transplant procedure is the conditioning regimen, which uses high-dose chemotherapy or radiation treatment to get the patient's body ready for the transplant. The training program accomplishes several significant goals:
- High-dose chemotherapy or radiation treatment is used to eradicate any cancerous or diseased cells present in the patient's body.
- The patient's immune system is suppressed by the conditioning routine, which aids in preventing the rejection of the transplanted cells.
- The patient's bone marrow is given more room by the conditioning regimen so that the transplanted stem cells can expand and generate new blood cells.\
- Depending on the patient's condition and the sort of transplant being done, the exact medications and doses used in the conditioning regimen may change. The conditioning routine may have negative side effects for patients, such as fatigue, hair loss, nausea, and vomiting. Throughout and after the conditioning program, the patient's medical team will closely monitor their condition to manage any side effects and ensure they are prepared for transplantation.
Process for Transplanting Bone Marrow
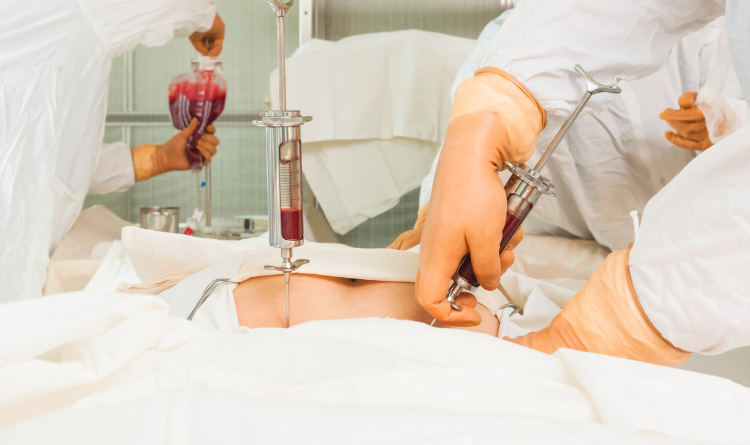
A bone marrow transplant process consists of the following steps:
- The patient is subjected to a series of exams and assessments prior to the transplant to ascertain their suitability for the operation. A donor is chosen and assessed if an allogeneic transfusion is intended.
- Apheresis or bone marrow harvesting is used to obtain stem cells from a patient or a volunteer. The stem cells are then kept in storage until a transfusion is required.
- High-dose chemotherapy or radiation treatment is used as part of the patient's conditioning regimen to eradicate any cancerous or diseased cells and make room for the infused stem cells.
- The patient receives the stem cells through an IV tube through transplantation. Once in the patient's bone marrow, the stem cells start to produce new blood cells.
- For several weeks or months following the transplant, the patient is under careful observation to manage complications and ensure the stem cells are successfully implanted. The healing process can take a while and may entail being hospitalized for several weeks or months while receiving close medical attention.
The patient can experience side effects from the conditioning program and the transplant itself during the operation, such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, fever, and infection. To guarantee a successful transplant, the patient's medical team will carefully monitor their condition and manage any side effects.
Following Transplant Treatment
A crucial step in the bone marrow donation procedure is post-transplant care. The patient's immune system is compromised after the donation, leaving them more susceptible to infections and other problems. To ensure the transplanted stem cells are working correctly and to handle any complications or side effects, the patient will need ongoing medical care and monitoring.
The patient may need to remain in the hospital for several weeks or months following the transplant in order to receive close medical supervision and supportive care. Infection, graft-versus-host disease, and other problems will be kept an eye on in the patient. Additionally, they will be given medicine to treat any side effects and stop the transplanted cells from being rejected.
The patient must take preventative measures, such as avoiding interaction with sick individuals and using good hygiene to avoid infections. They might also need to refrain from taking any medications, hobbies, or foods that could compromise their immune system.
Risks and Possible Complications
This complicated medical procedure carries a high risk of complications and adverse effects. Risks and possible complications connected to BMT include –
- Graft-versus-host disease is a frequent complication that happens when the patient's own organs are attacked by the transplanted stem cells. Skin rashes, diarrhea, liver failure, and other severe complications are all possible outcomes of GVHD.
- Due to a compromised immune system, patients who undergo BMT are at a greater risk of contracting infections. These illnesses can be severe and may need to be treated in a hospital.
- The conditioning regimen's high-dose chemotherapy or radiation treatment can harm the patient's organs, including the lungs, liver, and kidneys.
- Anemia and hemorrhage are both possible side effects of BMT that can reduce blood cell production.
- In some cases, the patient's immune system may reject the transplanted stem cells, which can lead to severe complications and possibly necessitate additional medical care.
- BMT can raise the possibility of getting cancers like lymphoma or leukemia as a secondary condition.
- The worry and uncertainty related to BMT can result in issues like anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder.
Long-Term Impacts and Post-Procedure Treatment
Patients may experience long-term effects following a bone marrow transplant that require continuing medical supervision and care. These outcomes include the following –
- A long-term side effect that can develop after BMT, it can manifest as several symptoms, including skin rash, dry eyes, and joint discomfort. Chronic GVHD may require continuous medical attention and treatment for some years.
- BMT has the potential to lead to infertility in both males and women. Before receiving BMT, patients who intend to have children may need to consider fertility preservation alternatives.
- BMT can raise the possibility of having thyroid issues, which may call for ongoing medical observation and care.
- BMT can harm the lungs, creating breathing issues and necessitating ongoing medical attention.
- BMT can raise the possibility of getting cancers like lymphoma or leukemia as a secondary condition.
Top Bone Marrow Transplant Hospital in India
In India, many renowned hospitals provide bone marrow transplant services. Some of the best bone marrow donation facilities in India are listed below –
- Indraprastha Apollo Hospital New Delhi- The hematology department of the hospital is counted among the top 10 hematology hospitals in India, well-equipped with state-of-the-art techniques for non-invasive vascular testing, diagnostic angiography, and endovascular therapeutic procedures.
- Fortis Memorial Research Institute, Gurgaon - Fortis is a well-known healthcare institution in India and is best known for Bone Marrow Transplants. Well-equipped HEPA filters, isolation wards, a laminar airflow system, and a safe hospital environment increase transplants' success rate. They have the experience and trained medical professionals dedicated to their patient's well-being.
-
Apollo Hospitals, Greams Road, Chennai- Apollo Hospital is known for its excellent outcomes and successful track record in the area of Bone Marrow Transplants. The hospital offers personalized care to its patients. The medical team of the hospital not only helps patients during their transplant and supports them with post-transplant care. They do the best possible things to make patients' life healthy.
- Medanta - The Medicity in Gurgaon - Medanta is the most preferred destination for patients who want to do a Bone Marrow Transplant. The hospital has a dedicated and compassionate team of doctors, nurses, and other medical professionals that provide individualized health care to their patients. They are experts in their fields and have the best knowledge of the latest advanced technology.
These hospitals have cutting-edge equipment, qualified medical staff, and a high percentage of bone marrow transplant success. A group of skilled physicians and a specialized bone marrow transplant center are available at these hospitals.
Success Rate

The probability of reaching a desired result of a medical condition or treatment is referred to as the success rate. The difficulty of the condition, the patient's age and health state, the type of treatment used, and the stage of the disease are just a few of the critical factors that affect the prognosis and success rate of a medical condition or treatment.
It depends on the type and stage of cancer; the success rate of chemotherapy can vary from 20 to 80%. Similarly, a patient's prognosis for heart failure may change based on how serious the disease is and how well the treatment works.
Conclusion
Bone Marrow Transplant is a complicated medical procedure that requires the replacement of damaged bone marrow with healthy stem cells. It is a lifesaving treatment for those who are suffering from different types of blood disorders, including leukemia, lymphoma, and aplastic anemia.
However, present medical infrastructure, advanced medical technology, the best hospitals, and their medical team make this complicated task easy and possible for the patients. Hospitals are now focusing on offering patient-centric treatment that helps achieve a high success rate and improve patient outcomes. It is a hope for a cure and a better quality of life for the patients.