What Is Breast Cancer?
Breast cancer starts when cells in the breast start to grow out of control & form a tumor. This is a malignant tumor that grows into the surrounding tissues or spread into distant areas of the body.
Lobular carcinoma: Is the one which starts off in the lobules.
Ductal carcinoma: Is the one which begins from the ducts.
This is the most common cancer in females worldwide.
Get in Touch with Medical Experts
Overview OF BREAST
Breast is a mass of fatty and glandular connective tissues. It is composed of :- 
-
Lobules: produces milk.
-
Ducts: that carries milk from lobules to nipples.
-
Fatty tissues.
-
Areola: pink or brown circular area that contains small glands and secretes moisture as a lubricant.
-
Connective tissue & Ligaments: provide shape &support to the breast
Breast mechanism
Development of female breast does not begin growing until puberty. At this stage, the breasts starts responding to the increased estrogen and progesterone hormones in the body. Development of breast ducts and milk glands also begin in puberty.
-
Estrogen: is the hormone responsible for development of female sexual characters like breast. In the first part of menstrual cycle, this hormone stimulates the growth of the milk ducts
-
Progesterone: is other female hormone, which prepares the uterus for pregnancy and produces milk for lactation. In second part of the cycle, this hormone stimulates the lobules.
During menopause both these hormones declines, but the adrenal glands continues to produce estrogen so that the sexual characters are maintained.
FUNCTIONS OF BREAST
Is to produce, store and release milk to lactate the baby. It provides complete nutrition for the newborn baby as it contains carbohydrate (lactose), fats and proteins as well as micronutrients.
Breast Cancer Causes
There are many conditions that may lead to breast cancer, some of them are -
-
Family history of breast cancer or any other related cancer history
-
Reproductive history
-
Exposure to ionizing radiations
-
Oral contraceptives
-
Smoking
-
Alcohol
-
Obesity
-
High socioeconomic status
-
Hormone replacement therapy
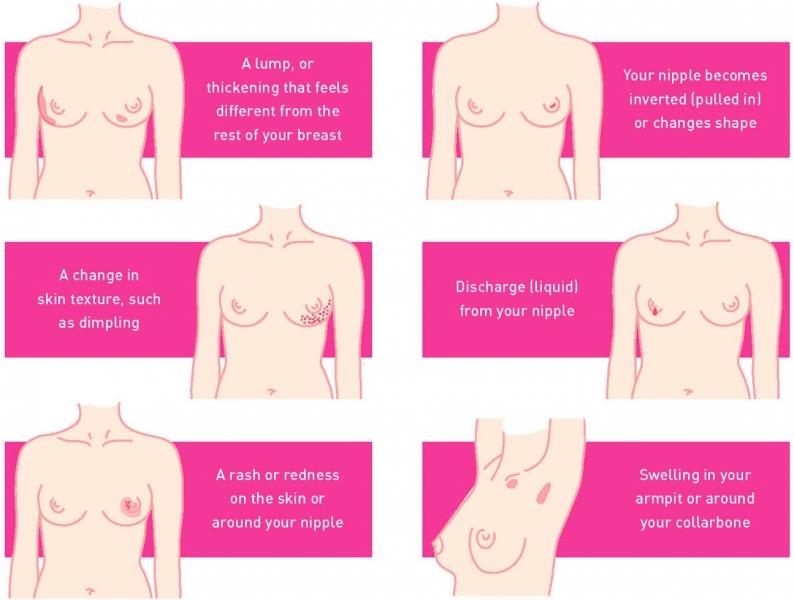
Signs and Symptoms
Breast cancer symptoms vary widely which may be from lumps to swelling to skin changes. Lot of times several breast cancers have no obvious symptoms at all. Symptoms that may be similar to those of breast cancer may be the result of non-cancerous conditions like infection or a cyst.
EARLY SIGNS
-
Hard & irregular lump in the breast, which does not go away and is attached to the skin or the chest wall.
-
Lump in the axilla
-
Changes in breast shape or size
-
Skin changes-orange peel skin or peau d orange
-
Redness & swelling
-
Nipple discharge
-
Crusting, ulcer or scaling
LATE SIGNS
-
Bone pain
-
Nausea
-
Loss of appetite & weight loss
-
Jaundice
-
Headache
-
Double vision
-
Muscle weakness
Diagnosis
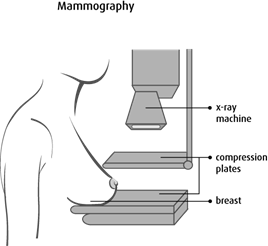
Diagnosis will be based on Patients history, Physical examination and Investigations
Detailed history- includes signs, symptoms and any associated risk factors
Physical examination- includes complete (clinical) breast examination along with examination of other systems.
Investigations - includes
-
Mammography
-
Ultrasound
-
Biopsy - FNAC
-
Lymph node biopsy
-
Liver ultrasound
-
Blood chemistry test
-
Bone scan
-
Chest x-ray
Mammography
-
Complete blood count
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
STAGING
Staging defines the extent of the cancer in the patient's body and is based on
-
Whether the cancer is invasive or non-invasive
-
Size of the tumor
-
Lymph nodes are involvement and count
-
Diagnosis of metastasizing (spread to other parts of the body)or not
TNM (Tumor, Nodes, and Metastasized) staging system
This system is the most preferred cancer staging system in use. Others systems are more specific to a particular type of cancer.
-
In situ: Presence of abnormal cells, which have not spread.
-
Localized: Cancer is limited to the breast
-
Regional: Lymph nodes principally those present in the armpit are involved
-
Distant: Cancer has spread to the other parts of the body.
Metastasis
Is a process in which a tumor is able to successfully spread to the other parts of the body and grow there, invading and destroying the other healthy tissues. The resulting condition is a serious one & it is very difficult to treat.
The most common site of spread of breast cancer is:
-
Regional lymph node
-
Chest wall
-
Skin of breast
-
Liver, lung brain
PROGNOSIS AND SURVIVAL
Prognosis is an estimate given by the doctor of how the cancer will affect a patient and how will it responds to the treatment.
The following are prognostic and predictive factors :-
-
Stage
-
lymph node status
-
Tumor size
-
Tumor grade
-
Type of tumor
-
lymphatic and vascular invasion
-
Age of the patient
TREATMENT
The average breast cancer treatment cost in India is around 3,000 USD while in Turkey it starts from 4,500 USD. Treatment options for breast cancer are as follows:
Surgery:
-
Breast conserving therapy and radiation therapy
-
Modified radical mastectomy
-
Maxillary lymph node dissection
-
Sentinel lymph node dissection
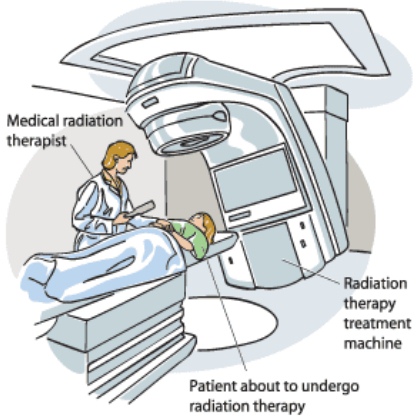
| Radiation therapy: controlled doses of radiation are targeted at the tumor to destroy cancer cells.
|
|
| Chemotherapy: medications are used to kill the cancer cells. These are called cytotoxic drugs. |
|
-
Hormonal therapy: it may help curb the growth, spread or recurrence of some type of cancer. It helps shrink or slow the growth of advanced-stage
-
Biological therapy: it helps to use the body immune system to curb the cancer. It involves using substances derived from living organisms, or laboratory-produced versions of such substances to treat cancer. Some biological therapies for cancer use vaccines or bacteria to stimulate the body's immune system to act against cancer cells.
-
Bisphosphonates: These are the drugs that slow down or prevent bone damage. This treatment is done when cancer has spread to the bone from another part of the body
Follow up: it is regular to have follow ups especially after first 5 years of treatment.
Breast Cancer Treatment in India
As a medical travel destination, India provides its patients with the best treatment at a low cost. With its advanced oncology hospitals and expert oncologists, the country gives you several options for your treatment.
Equipped with the latest medical equipments, advanced laboratories, ICUs, operation theatres, cath labs, emergency units the oncology hospitals provide their patients with everything that they need for their treatment.
The Indian oncology doctors are also experts in their field. They not only provide their patients with proper diagnosis but also aim for speedy recovery of the patient.
Know More:
Best Cancer hospitals in India
Cost of Breast Cancer Treatment in India
Breast Cancer treatment is the most pocket friendly in India. As the treatment procedure progresses, its cost is also divided into certain segments, which are:
Biopsy or PET scan: Costs around USD 1000
Chemotherapy: Costs approximately USD 1500
Surgery: Costs between USD 4000 - 6000
Note: The above procedures are taken only when prescribed or suggested by the oncology doctor. But a biopsy is mandatory without which cancer will not be detected.
The cost of breast cancer is determined by the type of therapy used. India is one of the leading destinations for breast cancer treatment and that's why every year numerous of patients travel to India for their treatment at a competitive price.
Know more about the cost of cancer right here.
PREVENTION
Some lifestyle modifications can significantly help in reducing women’s risk of developing breast cancer. These are as follows:
-
Reducing alcohol consumption
-
Physical exercise
-
Well balanced & healthy diet
-
Healthy body weight
-
Postmenopausal hormone therapy
-
Breast feeding reduces risk of breast cancer
Facts on Breast Cancer
It is the second leading cause of death in women worldwide
-
It is a malignant tumor that develops in the cells of the breast
-
It can occur both in men & women, but its more common in females
-
The first sign of breast cancer is mostly a breast lump or an abnormal mammogram
With an increase in public awareness, the prognosis & survival rates of people diagnosed with breast cancer has improved significantly
If breast cancer is diagnosed in its early stages, that is before it has spread, then the five-year survival rate is approximately 98.5 percent. If the cancer has metastasized and is in advanced stage, that survival rate falls to approximately 25 percent.
Five steps for self examination
Breast self-exam is a way that a female can check their breasts for any abnormal changes (such as lumps or thickenings). This includes looking at the breast and feeling the breast. Any unusual changes noticed should be immediately reported to the doctor. If breast cancer is detected at an early stage, then the surviving chances are greatly improved.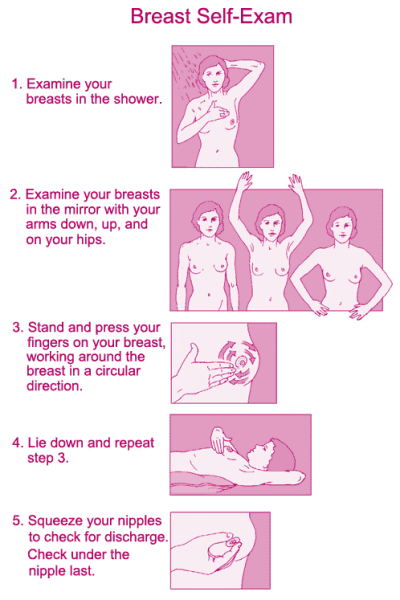
Step 1 : Start by looking at your breasts in the mirror with shoulders straight and arms on the hips. Look for:
Normal
-
Breasts are of their usual size, shape, and color
-
Breasts are evenly shaped without visible any distortion or swelling
Abnormal Changes
-
Dimpling, puckering, or bulging of the skin
-
Nipple that has changed its position or an inverted nipple (pushed inward instead of sticking out)
-
Redness, soreness, rash, or any kind of swelling
Step 2 : Raise the arms and look for the same changes mentioned in Step 1.
Step 3 : look for any signs of fluid coming out from one or both the nipples (this could be a watery, milky, or yellow fluid or blood).
Step 4 : lie down on the floor & feel the breasts, by using the right hand to feel the left breast and then the left hand to feel the right breast. Use a firm, smooth touch with the help of first few finger pads of the hand, keeping the fingers flat and together. Then use circular motion, about the size of a quarter.
-
Cover the entire breast from top to bottom, side to side, from your collarbone to the top of your abdomen, and from your armpit to your cleavage. A pattern should be followed to be sure that the entire breast is covered.
-
Begin from the nipple, moving in larger and larger circles until you reach the outer edge of the breast. Fingers can also be moved up and down vertically, in rows, as. This up-and-down approach seems to work best for most women.
-
Make sure to feel all the tissue from the front to the back of the breasts. Use :
-
Light pressure: for the skin and tissue just beneath
-
Medium pressure: for tissue in the middle of the breasts
-
Firm pressure: for deep tissue in the back.
-
Once reaching the deep tissue, patient should be able to feel down to the ribcage.
Step 5 : Lastly, feel the breasts while standing or sitting. Most of the females find that the easiest way to feel their breasts is when their skin is wet and slippery, so they prefer to do this step in the shower. Breast should be examined the same way like in Step 4.