Breast Cancer is a life-altering diagnosis that can be both emotionally and financially draining. While the medical industry has made significant progress in diagnosing and treating Breast Cancer, the costs of the treatments can be substantial.
Breast Cancer has high public health importance and impact on Germany. It is the most common cancer in women (57,000 cases yearly, 27.8% of all registered female cancers). Although survival after Breast Cancer is rather good (5-year relative survival rate 81%), every year, about 18,000 women die of Breast Cancer. Breast Cancer treatment costs almost 2 billion Euros per year (0.8% of the total health costs).
Germany is known for its advanced healthcare system and state-of-the-art medical facilities, making it a popular destination for patients seeking high-quality medical treatment.
Get in Touch with Medical Experts
What is Breast Cancer?
Breast Cancer is a disease in which the breast cells grow out of control. There are different kinds of Breast Cancer. Breast Cancer types depend on the cells which turn into cancer. It occurs almost entirely in women, but men can get Breast Cancer, too.
Breast Cancer can start in different breast parts. A breast is made up of three parts:
- Lobules are glands that produce milk
- Ducts are tubes that carry milk to the nipple
- Connective tissue surrounds and holds everything together
Most Breast Cancers begin in the ducts or lobules.
Breast Cancer, spreading outside the breast through blood vessels and lymph vessels, is said to have metastasized.
Know some facts about breast cancer:
What are the Types of Breast Cancer?
The most common type of Breast Cancer are:
- Invasive ductal carcinoma begins in the ducts and then grows outside the ducts into other parts of the breast tissue. It can metastasize or spread to other body parts.
- Invasive lobular carcinoma starts from the lobules and then spreads to the close by breast tissues. These cancer cells can also spread or metastasize to other body parts.
- Paget's disease, medullary, mucinous, and inflammatory Breast Cancer are other less common kinds of Breast Cancer.
- Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS), a breast disease, may lead to invasive Breast Cancer. The cancer cells, present only in the lining of the ducts, do not spread to other tissues in the breast.
What are the Symptoms of Breast Cancer?
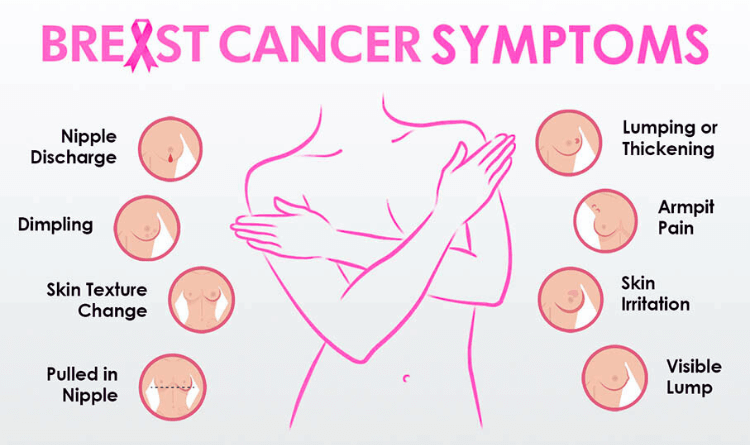
Signs and symptoms of Breast Cancer include:
- A breast lump or thickening of part of the breast.
- Change in the shape, size, or appearance of the breast
- A newly inverted nipple
- Dimpling (changes to the skin over the breast)
- A new lump in the underarm or breast
- Discharge from nipple (including blood) other than breast milk
- Pain in any area of the breast
- Risk Factors of Breast Cancer
Risk Factors of Breast Cancer
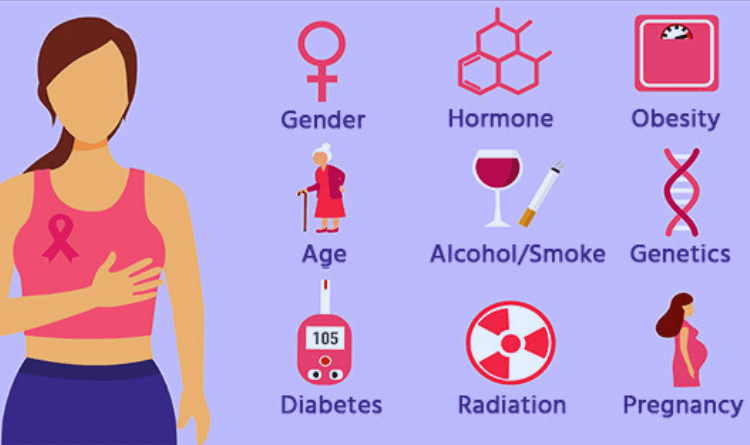
- Age: As most Breast Cancers are diagnosed after age 50, the risk for Breast Cancer increases with age
- Genetic mutations: Women who possess mutations in specific genes, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2, are more likely to develop Breast Cancer.
- Reproductive history: Menstrual cycles before 12 and menopause after 55 raise the risk of getting Breast Cancer.
- Family history of breast/ovarian cancer: The risk of Breast Cancer increases if she has first-degree relatives or multiple family members having breast/ovarian cancer.
- Personal history of Breast Cancer or certain non-cancerous breast diseases increases the risk of getting Breast Cancer a second time.
- Women who had radiation therapy to the chest or breasts before age 30 have an increased risk of getting cancer later in life.
How is Breast Cancer Treated?
Breast Cancer treatment in Germany includes various modifications of minimally invasive and radical surgical procedures, radiation therapy, and systemic treatment. Chemotherapy, hormonal, and targeted therapy are planned individually, based on Oncotype Dx™, MammaPrint® tests, ER and PR, HER2/neu receptor testing, and Ki-67 analysis.
Breast Cancer treatment depends on the kind and spread of Breast Cancer.
Surgery
The surgery removes the atypical tissues, including the primary tumor and any potentially affected lymph nodes. It also corrects any postoperative cosmetic defects. The surgeon removes the tumor and several nearby lymph nodes. This helps prevent a relapse of the malignant process.
To improve the accuracy of the operation, surgeons use the FDA-approved MarginProbe device, which allows the detection of any remains of atypical tissue in the surgical field and the removal of them.
Radical mastectomy is performed only when the tumor has spread to the pectoral muscles and axillary lymph nodes.
In some patients, the surgeon may prefer more sparing modifications of mastectomy:
- Skin-sparing mastectomy facilitates a subsequent autologous breast reconstruction
- Nipple-sparing mastectomy additionally preserves the nipple and areola
- Simple mastectomy preserves axillary lymph nodes and pectoral muscles
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer is carried in two ways:
- Neoadjuvant chemotherapy is prescribed before surgery. It helps reduce the tumor size so the surgeon can perform organ-preserving surgery without total mammary gland excision.
- Adjuvant chemotherapy is prescribed after surgery. It helps suppress cancer cells that remain in the body.
Prognostic genomic testing is widely used in German clinics. It determines the most effective systemic treatment regimen (monotherapy, combination chemotherapy, or a combination of chemotherapy with hormonal drugs). This includes:
- Oncotype Dx assesses the risk of relapse based on an analysis of 21 relevant genes
- MammaPrint evaluates the expression profile of 70 relevant genes
- PAM50 test examines 50 genes potentially associated with cancer recurrence
Hormonal Therapy
It blocks cancer cells from getting the hormones they need to grow. In 50-70% of women, breast carcinomas are hormone-sensitive and hormone-dependent.
Three types of hormones with fundamentally different mechanisms of action:
- Antiestrogens include Tamoxifen and its analogs
- Aromatase inhibitors include Letrozole, Aromasin, Arimidex, and their analogs
- Androgens includes Halotestin
Radiation Therapy
German clinics use five modes of radiation therapy for Breast Cancer:
- Preoperative radiotherapy in the form of an intensive or delayed course can destroy or damage malignant cells located on the periphery of the tumor.
- Postoperative radiotherapy affects the preserved lymph nodes (for example, supraclavicular or parasternal ones) and prevents cancer recurrence.
- Intraoperative radiotherapy (intrabeam technique) is performed during organ-preserving operations. The bed of the removed tumor and axillary lymph nodes are irradiated.
- Radiation therapy as an independent treatment method is carried out in cases of inoperable neoplasia or severe contraindications for surgical treatment. This option can also be used at the woman's request if she refuses an operation.
- Interstitial radiotherapy causes minimal damage to the surrounding healthy tissues.
Targeted Therapy
When planning a targeted therapy regimen, the doctors determine the number of specific receptors and indicators of the proliferative activity of cancer cells. This includes:
- HER2/neu: It is intensively produced in 20-25% of women with Breast Cancer. Should HER2 receptors be activated, the cancer cells will start their division, and the tumor will grow into healthy tissues and metastasize.
- Ki-67 protein is synthesized only in actively proliferating cells. The higher the levels of Ki-67, the more malignant the tumor is.
Why should you choose Germany for your Breast Cancer Treatment?
Treatment of Breast Cancer in Germany has several advantages:
- Modern equipment for diagnosis and effective therapy
- High qualification of doctors and other medical personnel
- The use of high-quality German drugs, as well as new protocols for chemotherapy and hormonal therapy
- Standardization of the whole process from diagnosis to rehabilitation
- A modern approach, the use of methods of minimally invasive surgical treatment of Breast Cancer
- Effective oncological rehabilitation programs after treatment
Cost Related to Breast Cancer Treatment in Germany
| Treatment name | Cost range |
| Breast Cancer | USD 18900 to USD 23100 |
| Chemotherapy | USD 1800 to USD 2200 |
| Breast Biopsy | USD 900 to USD 1100 |
Top Doctors in Germany Providing Breast Cancer Treatment
- Dr. Med. Marek Budner: He is a surgical oncologist with over 31 years of experience. His expertise lies in Breast diseases, Surgical treatment of Mammary carcinoma, Oncoplastic breast surgeries, Plastic and Reconstructive Breast Surgery, and Colposcopic diagnostics in the lower genital tract.
- Prof. Dr. Med. Karl-Jurgen Oldhafer: He is a surgical oncologist with over 33 years of experience. His clinical interest includes treating biliary diseases, gallbladder tumors, liver diseases, and cirrhosis.
- Prof. Dr. Med. Michael Bartels: He is a surgical oncologist with over 34 years of experience. His clinical interest includes Pancreatic surgery, Minimally Invasive Procedures, Hepatobiliary surgery, and Colorectal and Cancer surgery.
- Prof. Dr. Med. Martin Strik: He is a surgical oncologist with over 23 years of experience. His clinical interest lies in Oncological Surgery of Upper and Lower GI, Minimal Invasive Surgery, Pancreatic and Hepatic Surgery, Esophagus and Stomach Surgery, Colorectal Surgery (malignant and benign), Abdominal Soft Tissue Tumors (Sarcomas), Coloproctology, Endocrine Surgery, Thyroid Surgery, and Incisional Hernia surgery.
- Dr. Boris Pfaffenbach: He is a reputed Oncologist with over 28 years of experience. He performs Esophagectomy and offers chemotherapy for Leukemia and Breast Cancer.
Conclusion
The high quality of medical care and active use of innovative treatment approaches contribute to the fact that women from Europe, Asia, and Arab countries often seek medical care in German clinics. If your breasts have not been removed surgically, you must get a yearly mammogram. Depending on the treatment, you might also need other tests, such as regular bone density tests or heart tests. Whether you are a patient or a loved one of someone battling Breast Cancer, the information in this article can help you decide where to seek medical treatment.