Did you know approximately 8 to 18% of all women will develop ovarian cysts at some point? Ovarian cysts can range from simple to complex cysts that may or may not require treatment. These grow on or inside the ovaries. Regular pelvic examinations help in the early detection and management of ovarian cysts.
Gynecologists treat ovarian cysts. Various countries, including India, Germany, Turkey, and UAE, have some of the most renowned gynecologists in the world. Consulting a well-trained physician is necessary for high-quality results.
The cost of ovarian cyst treatment in India ranges from 1 to 1.5 lakhs, which is nominal compared to other developed nations. This blog will help you better understand what ovarian cyst is, how it is treated, and the treatment cost.
Get in Touch with Medical Experts
What is an Ovarian Cyst?
Ovarian cysts or adnexal masses are fluid-filled sacs developing on or inside the ovaries. These are very common and do not show any prominent signs and symptoms. At least one pelvic mass will develop in 20% of women in their lifetime.
Ovaries are 2 in number and serve the primary function of releasing an egg every 28 days (menstrual cycle) and releasing sex hormones (estrogen and progesterone). Ovarian cysts can affect either the ovaries or just one of them.
Most ovarian cysts are likely to go away naturally, but sometimes, they can grow bigger and cause complications like ovarian torsion and cyst rupture.
Since most ovarian cysts are not harmful, they require no specific preventive measures. However, regular pelvic examinations are necessary for the physician to find any cyst requiring treatment.
What are the Risks and Causes of Ovarian Cysts?
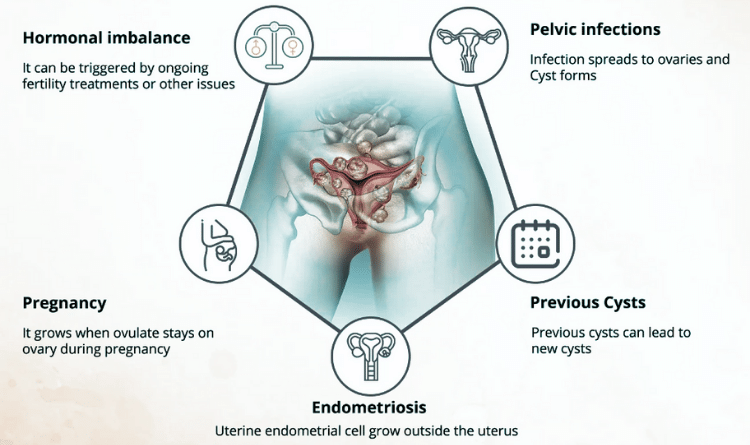
One of the significant causes of ovarian cysts is ovulation. Other causes include –
- Endometriosis: Chocolate cysts or endometriosis is the presence of lesions outside the uterus.
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease: If the pelvic infections are severe, there are chances that it may spread to the ovaries, causing cysts.
- Abnormal Cell Production: Cysts like cystadenomas and dermoids are formed due to atypical cell reproduction.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: PCOS, a hormonal disorder, causes several harmless small cysts to form in the ovaries.
There are numerous risk factors associated with ovarian cysts. Some of them are –
- Hormonal Problems: Taking fertility medicines like clomiphene or letrozole causes ovulation and increases the chances of cysts.
- Pregnancy: There are chances that the follicle formed when you ovulate stays on the ovary throughout the pregnancy. It can grow bigger and cause complications.
- Previous Ovarian Cysts: If you had one or more ovarian cysts in the past, you are more likely to have them in the future.
What are the Usual Symptoms of Ovarian Cysts?
As mentioned earlier, the majority of ovarian cysts do not show symptoms. However, if the cyst grows to a significant size, it shows signs like –
- Pelvic pain that ranges from dull ache to severe and sharp pain
- Pain during sex
- Frequent need of urination
- Heavy periods or irregular periods
- Bloating and swollen tummy
- Pain during bowel movements
- Difficulty getting pregnant
- Eating very little and feeling full soon
Ovarian cyst causes pain and severe symptoms when it –
- Becomes large
- Bleeds
- Breaks open
- Interferes with ovarian blood supply
- Gets twisted (torsion)
How are Ovarian Cysts Diagnosed?
Ovarian cysts are primarily found during pelvic exams and imaging tests like ultrasound. The physician will recommend further tests to determine the type of cyst, its size, and if it's solid or filled with fluid. Standard diagnostic tests include –
- Pregnancy Test (Serum hCG): Corpus luteum cysts are diagnosed during pregnancy tests.
- Pelvic Ultrasound: The test creates images and videos of the uterus and the ovaries on the screen. These images are used to detect the cysts' presence, location, and size.
- Laparoscopy: A small incision is made on the abdomen, and a thin, lighted tube (laparoscope) is inserted. The physician sees the ovaries using the laparoscope and looks for the cyst. If any cyst is found, it is removed during the same procedure.
- Tumor Marker Tests: The CA 125 blood test checks the levels of CA 125 protein. It is a cancer antigen whose blood levels get elevated when women have ovarian cancer.
What are the Different Types of Ovarian Cysts?
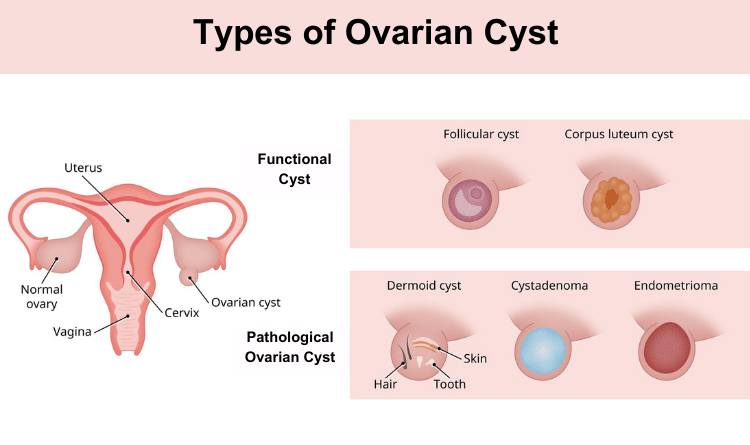
There are basically two types of ovarian cysts: functional cysts and pathological ovarian cysts.
- Functional Cysts: These are the most prevalent types of ovarian cysts unrelated to any disease. They are caused by ovulation. These cysts usually resolve on their own within 60 days.
- Follicular Cysts: During the menstrual cycle, the egg bursts out of its follicle, which then travels down the fallopian tube. A follicular cyst develops when the follicle does not rupture and release the egg.
- Corpus Luteum Cyst: Once the follicle has released the egg, it produces female hormones. It is now called the corpus luteum. Sometimes, the fluid gets built up in the corpus luteum, forming a cyst.
- Pathological Ovarian Cysts: These are formed due to abnormal cell growth and are less common.
- Cystadenomas: Formed on the surface of the ovaries, these cysts are filled with watery or mucus-like fluid. They have the potential to grow very large.
- Dermoid Cyst: Also known as teratoma, dermoid cysts are formed from the germ cells. Germ cells are the reproductive cells that make the egg. These cysts can have cells that make up the tissues like hair, skin, or teeth.
- Endometrioma is a cyst filled with the same fluid in the endometrium (lining of the uterus). These are also known as chocolate cysts, as the fluid resembles chocolate syrup.
How is Ovarian Cyst Treated?
The treatment of ovarian cysts depends on various factors like size and appearance, whether you have any signs and symptoms, and whether you have been through menopause.
- Watchful Waiting: Functional ovarian cysts go away on their own, usually within 8 to 12 weeks. They do not require additional treatment. A wait-and-watch approach is used for these cysts. A follow-up ultrasound is used to see if the cyst has resolved or not.
- Medicines: Oral contraceptives (birth control pills) are prescribed when patients suffer from frequent ovarian cysts. These medicines lower the risk of developing new cysts. However, no reports suggest these pills can decrease the size of already present cysts.
- Surgery: The surgery is needed when the ovarian cyst starts showing symptoms and increases in size. The kind of surgery that the surgeon will perform depends on the size and type of the ovarian cyst. Different types of surgeries that can be used are –
- Laparoscopy: Done for smaller cysts, it is a minimally invasive surgery performed using a laparoscope. The laparoscope helps see the ovaries and cysts are removed through minor cuts in the skin. Once the cysts are removed, dissolvable stitches are used to close the cut.
- Laparotomy: When the cyst is large, it is likely to be cancerous. In such cases, a laparotomy is used. The procedure involves making a single large cut in the abdomen, which gives better access to the cyst. The cyst and sometimes the ovaries also are removed and sent to the laboratories for further investigation.
If the laboratory findings confirm the presence of cancerous cells in the extracted cyst, you must consult a gynecological cancer specialist to get the ovarian cancer treated. Conditions like endometriosis and PCOS also lead to cyst formation and must be treated accordingly.
How Much Does Treating Ovarian Cyst Cost?
The cost of ovarian cysts varies from country to country. It also depends on the type of cyst and the treatment the patient receives. In India, the cost of ovarian cyst treatment is in the range of USD 2200 – 2700. The patient has to stay in the hospital for 1 to 2 days and is discharged after proper evaluation.
The cost of treatment in different countries is given below.
| Country | Cost |
| USD 1800 - 2200 | |
| USD 1800 - 2200 | |
| USD 6000 - 7000 |
Conclusion
An ovarian cyst is one of the most common gynecological diseases in which solid or fluid-filled sacs are formed in the ovaries. The general symptoms of the disease include pelvic pain, irregular periods, pain during sex, bloating, and difficulty getting pregnant. The condition is most likely to resolve on its own. However, in some cases, the cysts can grow bigger and may require surgical removal.