Dr. Vijayant Devenraj is a renowned Cardiothoracic and Vascular surgeon with over 11+ years of experience. Dr. Vijayant Devenraj, MBBS, MCh (CTVS) from KGMU, Lucknow has a vast clinical experience in CABG or Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting. He is known as one of the best cardiac surgeons in India. His expertise extends to Bentall Surgery, Valve Repair and Replacement Surgeries (DVR, MVR, AVR), Congenital Heart Lesions (ASD, VSD, PDA, RSOV, TOF), Lobectomy, Empyema, and many vascular surgeries such as Fem-pop Bypass, Fem-Fem Bypass, Thromboembolectomy, Vascular Injuries Repair, and Aorto-bifemoral Surgery. He is currently working with Apollo Medics Super Speciality Hospital, Lucknow.

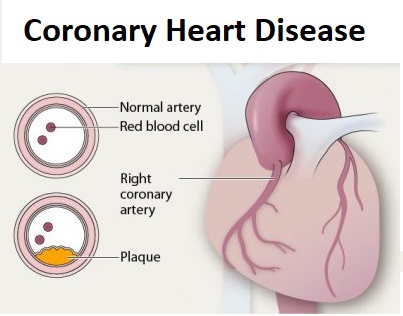
What is Coronary Heart Disease?
The heart works as a pump and supplies blood to all the organs of the human body for its proper functioning. To achieve this, the heart needs a steady flow of blood for circulation in the body. This steady supply of blood is maintained by the left and the right coronary arteries.
If these arteries are unable to supply a proper amount of blood to the heart for pumping, the entire process of circulation in the body is disrupted. This condition is called coronary heart disease where fat deposits in the form of plaque in the walls of the arteries, thereby constricting the blood flow and causing blockages. The plagues formed in the walls may tear and rupture the coronary artery and form clots. These clots can cause a heart attack.
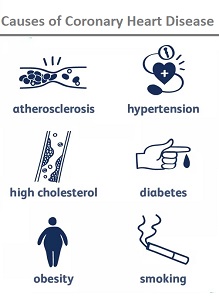
Causes of Coronary Heart Disease
Coronary heart disease ranks at the top of the list of heart diseases with India accounting for nearly 60 percent of the patients around the world. Coronary heart disease is caused due to:
- Age
- Obesity
- High fatty diet
- Smoking
- Genetic causes
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Alcohol consumption
Symptoms of Coronary Heart Disease
Unexplained fatigue to indigestion may all be a reflection of coronary disease and if left untreated, it may lead to heart failure. Here are some of the most common symptoms of coronary heart disease.
- Shortness of breath
- Pain in the chest
- Fatigue
- Swelling in feet and hands
- Persistent cough
- Fluid Retention
- Nausea/loss of appetite
- Fainting
- Irregular Heartbeat

Treatment of Coronary Heart Disease
Managing coronary heart disease with medication and lifestyle changes is desirable but not always possible, especially if the blockages are extensive. Surgical intervention remains the only treatment option in most cases. There are two ways to treat coronary heart disease:
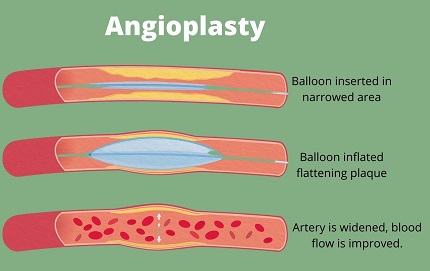
- Angioplasty – Inserting stents in the arteries with the help of a catheter to hold the blocked arteries open.
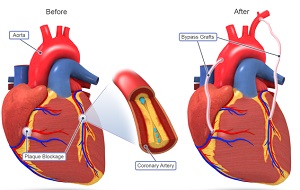
- CABG – Grafting of blood vessels to create an alternate route for the flow of blood to the heart.
Angioplasty: Angioplasty is a less invasive treatment option and requires a shorter hospital stay. The patient is usually not put under general anesthesia when undergoing angioplasty. However, angioplasty is not recommended if the blockages are spread across arteries or if the blood vessels near the heart have abnormal or altered structures.
CABG: CABG is a surgical procedure for treating coronary heart disease where a blood vessel from another part of the body is grafted to the affected artery bypassing the blocked portion. More than one graft may be inserted depending on the number of blockages present. The recovery time for CABG is longer and may require a hospital stay of about 7 days or more. The patient has to be put under general anesthesia and the entire operation may take up to 6 hours depending on the complexity of the presentation of coronary heart disease. Full recovery is expected in about a month or so.
These procedures can be done by an experienced cardiac surgeon in one of the best heart surgery hospitals in India.
Life After CABG or Angioplasty
A patient is expected to go back to his or her normal life after surgery sooner rather than later. For CABG it might take longer and certain sternal precautions may remain in force till the breastbone or sternum is completely healed. However, the important thing to note is that neither CABG nor angioplasty can stop blockages from reoccurring in the arteries if certain lifestyle changes are not invoked. For example, the following are necessary to manage coronary heart disease after surgery:
-
healthy fiber-rich, low-fat diet
- regular exercise
- quit smoking
- losing weight if necessary
- Managing stress
- Regular follow-ups with the cardiac surgeon
Conclusion
CABG or angioplasty should not be mistaken as a cure for coronary heart disease. It can only be managed with a combination of medication and a healthy regimen.